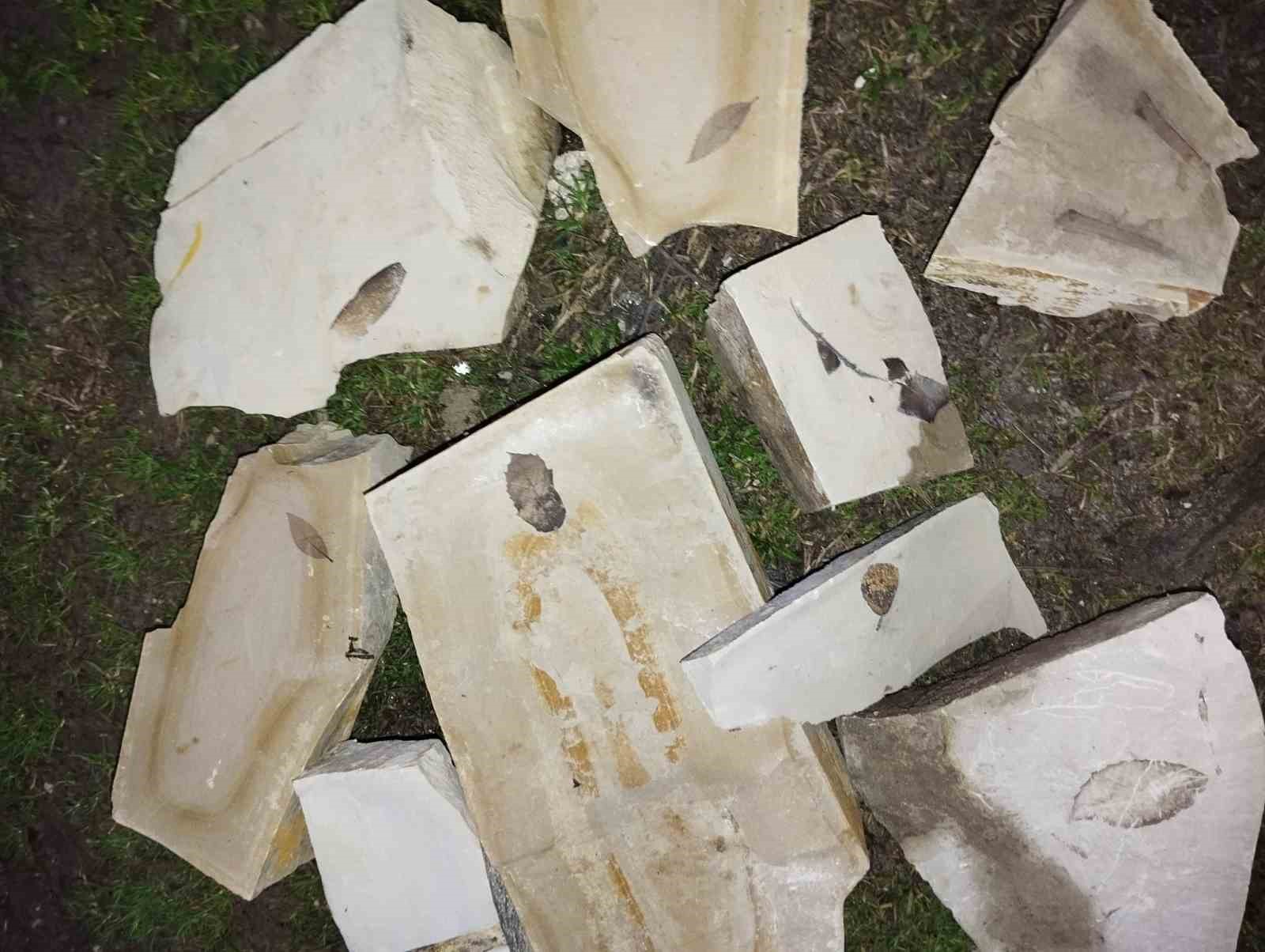

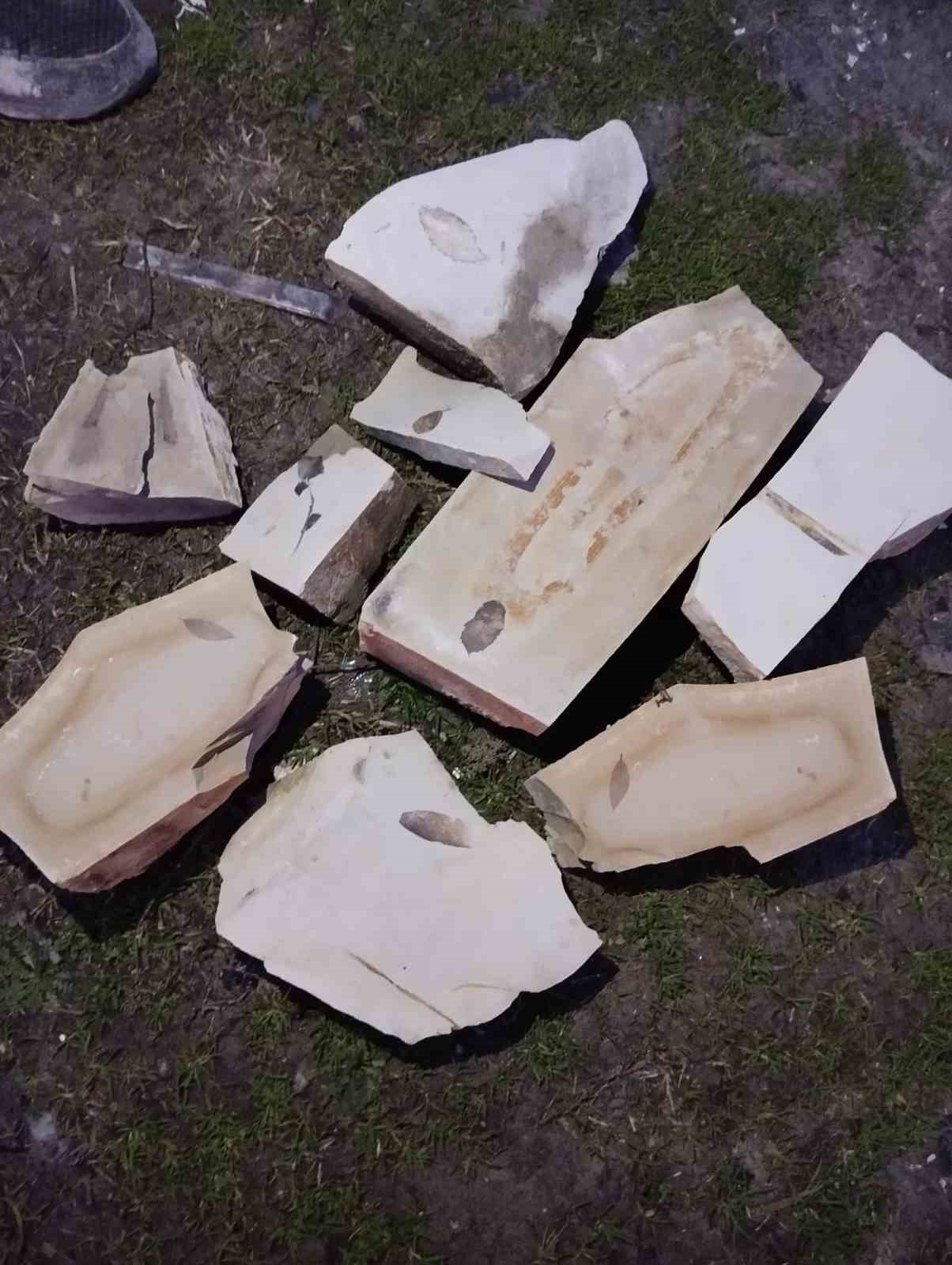
15 Million Year Old Leaf Fossils Discovered in Western Turkey
Leaf fossils estimated to be 15 million years old have been unearthed during field surveys between Yayla and Kirazlı villages in Kuşadası district of Aydın, Turkey. The fossils were discovered by Murat Uğur Sünetçi, a Geology Engineering student from Hacettepe University, while examining the rock structure of the area.
The leaf fossils, found within clayey limestone layers, were discovered through detailed observations. Geology Engineering student Murat Uğur Sünetçi said, “The leaves of plants that lived 15 million years ago were preserved along with the muddy and calcareous sediments of that period. Over time, these leaves fossilized within the clayey limestones.”
It is stated that the area where the fossils were found is a rich geological region with sedimentary accumulations from the Miocene period, and such findings provide important scientific data about the climate conditions and vegetation of ancient times. The fact that the leaf veins are clearly preserved further increases the value of the fossil. Experts state that this discovery is an important step in shedding light on the geological history of the Aegean Region, and the fossil samples will be sent to university laboratories for examination.

What is a Leaf Fossil?
Leaf fossils are the petrified remains of leaves from plants that lived millions of years ago. These fossils provide important information about the vegetation, climate conditions, and ecosystems of past eras. The formation and scientific significance of leaf fossils are as follows.
The formation process begins with rapid burial. After death, leaves are typically quickly covered by sediments such as mud, sand, or volcanic ash. This rapid burial prevents the leaves from decaying and ensures their preservation. Over time, the organic material of the leaf is replaced by minerals. During this process, the original structure and vein patterns of the leaf are preserved. After millions of years, this process results in the leaf becoming petrified and turning into a fossil.

The scientific significance of leaf fossils is evident in many areas. In terms of studying past climates, leaf fossils provide important clues about the climatic conditions of that time. For example, the shape and vein structure of the leaves can offer information about the temperature and humidity of the period. Regarding plant evolution, leaf fossils from different geological periods help us understand the evolution of plant species. Comparing extinct plant species with modern plants sheds light on evolutionary processes. In terms of geological history, leaf fossils are used to determine the age of the rock layers in which they are found, contributing to the creation of the geological time scale. For the study of ecosystems, leaf fossils help us understand the structure of past ecosystems, providing information about which plant species lived together and under what environmental conditions. Additionally, they offer insights into the vegetation that existed in the region where the fossils were found. This information demonstrates the crucial role of leaf fossils in both scientific research and the understanding of ecological history.
You may also like
- Archaeologists Discover 9,000-Year-Old Temple in Jordan Desert
- Sumerian Birth Certificate: One of History’s Oldest Records
- Archaeologists Uncover Unique Auditorium During Excavations in Sicily
- Astonishing 3,000-Year-Old Cave Paintings Unearthed in Brazil
- Ancient Assyrian Tablets: Science Uncovers 7th Century Writing Techniques
- The Mysterious Goddess of Levent Valley: 2800-Year-Old Hittite Goddess Figurine
- Discovery in Romania Reshapes History of Ancient Dacian Presence
- New Study: Climate Change May Have Played a Role in the Fall of the Roman Empire
- The Dazzling Treasure of Kibyra: The Medusa Mosaic Reopens to Visitors
- Stunning 2,500-Year-Old Settlement Discovered in North Macedonia









Leave a Reply