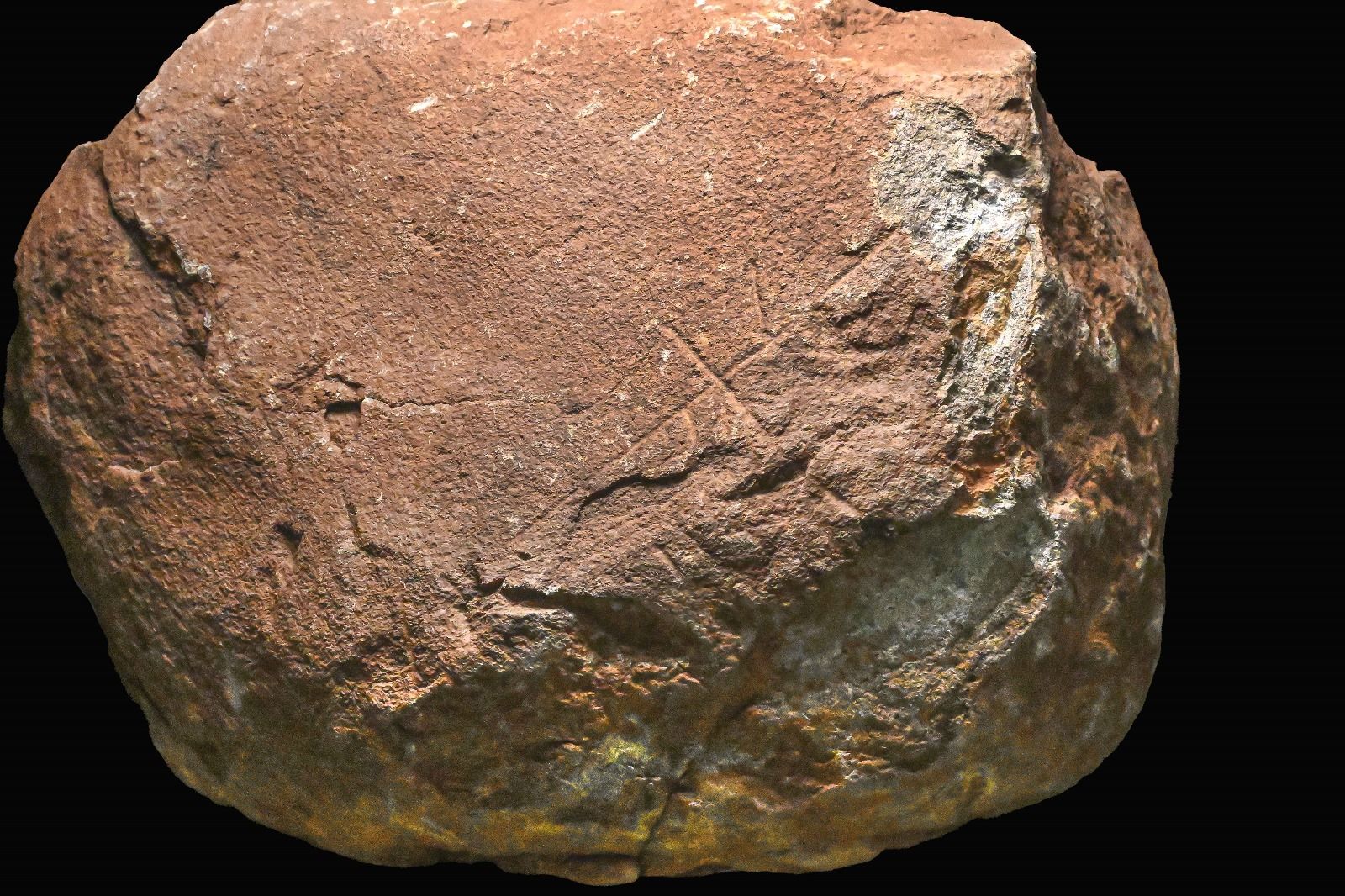
As part of the archaeological excavation at the Coto Correa site in Las Chapas, Marbella, the Ministry of Culture, Education, and Historical Heritage has reported the discovery of graphic designs on a stone block that could be more than 200,000 years old. This area, known for hosting the city’s oldest remnants, has been under archaeological protection since the accidental discovery of some stone tools from the Early Paleolithic period in the 1950s.
Traces of Prehistoric Art
The study and subsequent analyses have provided information about the geological evolution of the site, as well as shed light on the archaeological discovery of a series of stone tools carved into one of its layers. The set discovered in 2022 is highlighted by a gabbro block marked with lines, giving it an extraordinary character. The significance of this discovery is twofold: on one hand, it confirms the presence of settlers in Marbella during the Early Middle Paleolithic period, a period little known in Spain and unprecedented in the province of Malaga, where large flakes were found. Moreover, this unique stone with graphical representations of human origin could be 100,000 years older than the oldest cave art.
Scientific Studies Underway
The Ministry of Culture is conducting a study on this unique artistic document, aiming to confirm the relative dating proposed in the geoarchaeological study. The techniques applied for absolute dating consist of quartz analysis of different sedimentary samples, which will allow for a precise chronology of the samples to be established. Additionally, documentation work will be carried out using 3D scanning, which will allow for the creation of a high-resolution virtual composite of all the markings. This will allow for the examination of the entire surface in maximum detail, determining which work marks and graphics were used, providing an essential tool for the dissemination of results and publication in scientific journals.
Ongoing Research
The budget allocated for this phase of the research is 8,000 euros, and if the proposed dating is confirmed, Marbella will become a milestone in Paleolithic studies, beyond the municipality’s commitment to promoting archaeological research. Once the studies are completed, the Ministry of Culture will announce various events to present the discovery and its scientific results in detail.